What is Generative AI, and How Will It Disrupt Society?

The concept of generative artificial intelligence (GAI) poses a groundbreaking question that has until recently not been contemplated: at what stage does the relationship between humans and machines evolve from its present-day form into one that is so fundamentally changed that we can no longer regard one as being superior to the other when it comes to creative terms?
Humanity stands on the brink of a new technological revolution. It is poised to harness the full potential of AI and machine learning, allowing us to automate many tasks and systems, revolutionise communication, and conserve time and money in our daily lives.
Many are concerned that this could be the harbinger of a world full of robot overlords which would rob the human race of its free will. But what about those who will create those machines? In fact, as a futurist, I believe that in developing AI, we are creating a tool to enhance human cognition, giving us new means to think, invent and explore the universe rather than enslave humanity, although there are certainly some major challenges to overcome.
Let's explore what generative AI is, where it currently stands, and where it could potentially take us in the next years.
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI is a branch of computer science that involves unsupervised and semi-supervised algorithms that enable computers to create new content using previously created content, such as text, audio, video, images, and code. It is all about creating authentic-looking artifacts that are completely original.
In other words, generative AI is a subset of machine learning that focuses on creating algorithms that can generate new data. Generative models are used in many different application areas, from art and music to computer vision and robotics.
The term "generative" refers to how these models learn how to create new data rather than simply recognising it. For example, a generative model may learn how to generate images that look like faces given a certain number of parameters (such as the number of eyes or hair colour).
Futurum Research's principal analyst, Shelly Kramer, describes generative AI as a "means of making computers self-aware using data sets from multiple sources." She also explains that generative AI will be cheaper, faster, and better in some cases than what humans create by hand.
"The AI will then be able to identify and learn patterns over time, which can be used in incredibly cool ways, perhaps the most exciting of which is that it will be able to create data that does not even exist," Kramer concludes.
By using generative artificial intelligence, computers can generate or output new content by abstracting the underlying patterns associated with input data.
In the near future, machines can write, code, draw and create with credible, sometimes superhuman results because of a new class of large language models.
The Benefits of Generative AI
Generative AI is one of the most promising areas of artificial intelligence research. It's a field that can help us build computers that can perform tasks so complicated that they are currently beyond the reach of traditional algorithms.
Bringing generative AI to life will enormously benefit society — from helping us solve our most pressing problems to improving the human experience by creating new art forms and entertainment.
Here are some of the ways generative AI can make our lives better:
- The output is high-quality since it is generated through self-learning from multiple data sources. For example, a sentence could be generated from information found on Wikipedia and thousands of other websites. In this way, the system can learn to use complex grammar rules without being programmed beforehand.
- Reduces project-related risks. Generative AI uses algorithms to create designs that can be customised to fit any project. This enables the design team at a firm to create multiple versions of a building or structure and test them against one another to see which one works best.
- It improves the accuracy of machine learning models by using less biased models. This is because generative AI does not require any training data; instead, it generates its own training data based on input.
- The reduction of depth can be achieved without sensors. The ability of robots and computers to perceive the outside world as a human would is called "depth" in AI. Generative AI could be so sophisticated that it would no longer require the input of sensors or other external data sources to learn about its surroundings. Generative AI will be able to learn from experience and other sources. It can develop new ideas without any human intervention. This technology could be used in facial recognition, image classification, and image segmentation applications.
- Robots can understand abstract theories better in the real world and simulated environments. This is based on the idea that an AI can learn from a set of examples and then use that knowledge to create new things.
The Scope of Generative AI
Our ability to create things is one of our strongest traits. However, thanks to generative AI, almost every field requiring humans to create original content is up for reinvention, whether social media, gaming, advertising, graphic design, product design, or marketing. There is no doubt that generative AI will eventually become cheaper and faster, and better than what humans can create manually in some cases. While generative AI may replace certain functions completely, other functions will likely thrive through a tight iterative creative process between humans and machines.
Still, it will improve performance and reduce costs across a broader range of applications. It can be a tool to make things easier without substituting the entire creation process. In the ideal world, generative AI would reduce the marginal cost of creation and knowledge work to zero, resulting in massive productivity, wealth, value, and corresponding market capitalisation.
There are billions of workers engaged in knowledge and creative work, which is one of the focuses of generative AI. These workers can become more productive and creative by at least 10% using generative AI: they will work faster, more efficiently, and be able to handle more tasks at the same time. In this sense, generative AI can generate trillions of dollars in economic value.
Does now seem like the right time?
A generative AI approach shares the same "why now" as AI more generally: more data, better models, and increased computing power. As fast as the category changes, it is worth recapping the recent history in broad strokes to put the current moment in perspective.
What is Its Origin?
Over the years, Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have become the most popular generative AI model thanks to a great deal of research and practical applications. GANs were initially developed by Ian Goodfellow and his colleagues at the University of Montreal in 2014. The GAN architecture was described in a paper titled "Generative Adversarial Networks", and I have previously covered GANs.
Why is Generative AI Now a Reality?
Three primary factors contribute to the growth of generative AI: improvements in models, better and more data, and greater computing capacity.
Recent years have seen an increase in sophistication in machine learning models. By using deep learning, computers can now learn complex patterns in data that were previously difficult for them to discover. This has greatly influenced generative AI.
A more data-rich machine learning model can be trained with more available data. A large pool of training data has been created due to the increasing ubiquity of tools, software, and devices that generate data, such as the thousands of pictures you take with your smartphone, which are stored in the cloud or on social media. In short, computers have become much faster and more powerful in the last few years. Which ultimately means that they can do more things than ever before.
The Importance of Data for Generative AI Developments
In today's world, the amount of data we have access to is growing exponentially.
The overall amount of data created last year in the world was approximately 79 zettabytes. This number will likely increase over the next years. The majority of this data comes from many places, including common ones like social media, e-commerce, and search engines such as Google, Amazon, and Netflix. In addition to this, we can also expect more data from areas such as healthcare and financial services thanks to the Internet of Things (IoT).
Generative AI uses all this information to train its systems to perform human tasks, such as translating documents or identifying objects in photos and videos. For example, generative AI can be used to create realistic images of animals or people. This could be very useful in training self-driving cars to recognise things on the road.
As more data becomes available, generative AI will become even more important. There are many ways that this can happen:
More companies are collecting data from users' smartphones and other devices, which provides more information about what people like and do online. More companies are also collecting data about their customers' behaviour offline (in stores or on websites) and combining it with online data to get a complete picture of their customers' needs and interests.
In a nutshell, the rise of generative AI is due to the amount of relevant data available that contributes to the learning process. The more data we have, the better our algorithms can learn from it, and the amount of images, videos, text and code publicly available online is vast and growing exponentially (whether AI developers can use this content without asking permission is a different ballgame and something that will likely be food for many lawyers). The key is ensuring that we have enough data for our algorithms to learn from to be useful in real-world applications.
Characteristics of Generative AI
In the past, AI has been used to create simulations of reality or to simulate natural processes, such as learning how to play chess or Go. But in generative AI, machines learn how to generate art, music, and other forms of creativity — without human intervention or often simply by inputting a string of text.
Artificial intelligence can already write news articles and compose music; it can even paint pictures and design buildings. But unlike its predecessors, generative AI has no prior experience with any of these things; instead, it learns by itself based on data sets provided by humans.
Generative AI allows machines to create new works based on what they have learned from others. This opens up possibilities for artists and designers who want their work to be unique — but also for people who want their creations generated by machines for a specific purpose.
For these reasons, generative AI consists of two main elements:
Autoencoders
Autoencoders are made of an encoder, which maps the input data into a latent space; a decoder that reads from this latent space and generates new data points; and an objective function. The autoencoder learns by minimising its distance from the original dataset.
Generative Adversarial Networks
GANs are a type of machine learning framework in which two neural networks compete. AIs are given a training set to generate new data with the same statistics as the training set.
As a result, this technology presents groundbreaking characteristics:
- It is self-learning: Unlike traditional AI, generative AI can learn without being programmed. This makes it more flexible and adaptable to different environments and more efficient at solving problems.
- It uses unsupervised learning: Generative AI systems can also learn without being told what they should do or how to do it. This is called unsupervised learning, allowing them to discover hidden patterns in data without human intervention.
- It uses anomaly detection: Anomalies are instances where something does not make sense or deviates from what we expect based on our prior knowledge of a subject matter or topic area. Generative AI systems can detect anomalies in data sets and respond appropriately.
- It uses problem-solving: Generative AI systems can solve complex problems without human intervention because they can come up with innovative solutions or approaches based on their experience with similar problems in the past. For example, writer's block is one of the most common conditions in the creative industries. It can be caused by a lack of inspiration or from the writer being too close to the project and unable to see its flaws. With generative AI, we can draw new ideas and concepts from a set of seed inputs, avoiding leaving the page blank. So it can be said that generative AI is a tool to solve various problems within the normal creative processes in many industries.
An Overview of Generative AI Applications and Startups
The concept behind generative AI is quite straightforward. In this article, I will give an overview of several popular applications related to this subject that are currently revolutionising the tech industry.
Marketers, educators, healthcare professionals, artists, and everything in between, can all benefit from the use of generative AI. Using it, one could fabricate news stories or create original content, such as blog posts, music, movies, data reports, and so much more.
Example One: Using the medical profession as a case study
Creativity is the ability to generate new ideas and make them useful. Creativity is the ability to create something that has never existed before. It's not just one person coming up with a unique idea but rather a process of idea generation that may involve many people. Creativity is often thought of as a trait that only some people have, but it's a skill that anyone can learn and develop.
With that said, creativity is an essential part of life because it helps us solve problems and deal with unexpected events. We use creativity when figuring out how to approach a problem or situation we've never encountered before. It also helps us understand what other people are thinking and feeling, which allows us to find common ground and get along better with others.
Creativity is not just about art or music — it is found in all walks of life: science, business, and education; at home, at work, and at school; in sports, cooking, and gardening. Creative people think outside the box to find new ways of doing things better than before.
When we understand creativity in this way, we understand the impactful potential that generative AI can have on content creation, not only in the creative areas we are used to but in many industries, including healthcare. An excellent example of this is the creation of new medical images, such as those used in retinopathy diagnosis (which is the leading cause of preventable blindness. It is caused by damage to the blood vessels of the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye (retina)). Using it, doctors can create new patient records, which can then be incorporated into the system to improve accuracy.
To train these applications, they use large amounts of real-world patient data to learn deep learning techniques. Using these patterns generates new images. This process allows it to generate new data sets that humans could have never developed.
Ingenious AI-powered applications can create new content using existing information as the starting point. To improve accuracy, they can compare generated content with real-world data. Therefore, they can analyse large amounts of data efficiently and quickly, significantly improving their understanding of diseases.
Example Two: Augmenting data
Image augmentation is the most common data augmentation type. This scenario involves small changes to images, resulting in a more realistic image. For instance, you can change an image's brightness, contrast, saturation, hue, or colour balance. An image could also be rotated, flipped, cropped, or even zoomed in extremely, as they do in police detectives.
We can train neural networks using generative AI without having access to all the training examples since it enables us to train without sample data. It provides enough examples for the network to learn the problem's underlying structure. Following the model's learning, we can generate additional samples based on its knowledge.
How Are Market Leaders Using Generative AI?
There is a tool for turning text into speech offered by Amazon Web Services called Polly. The service has three tiers. A basic version uses algorithms that have been tested and proven to work. In the middle tier, neural networks are used to deliver a neutral voice that is often heard in news narrations as a method for Neural Text-to-Speech (NTTS). With the third version, companies can make their own personalised voice for their brand so that only their products are associated with sound.
The Microsoft code repository's CodeAssist service suggests snippets of code that can fill gaps in a program. It is still meant as a simple assistant for humans, even though it appears to be much more intelligent than simple code completion. It's been trained on over one billion public, open-source code lines. Through its knowledge, it can transform a simple phrase or comment, like "fetch tweets," into a full function. In marketing literature, it is called "co-pilot," but when it comes down to it, you are in control.
Amazon also offers DeepComposer, an artificial intelligence that can create an entire song with a short melody. It is also designed to act as a personal assistant to a human who first composes some simple segments, followed by adjusting parameters for a machine learning algorithm. A wide range of common genres of music is pre-trained in the system.
Some of IBM's generative models are used in drug design. They are trying to train their AIs to think of new molecules that could work as drugs by training them to imagine the right shapes. They are specifically looking for antimicrobial peptides that can target specific diseases.
Game companies are adept at creating artificial worlds and telling stories based on them by their very nature. Among the major names are Nintendo, Rockstar Games, Valve, Activision, Electronic Arts, and Ubisoft. While they have been creating and deploying many similar algorithms, they are still developing advancements in terms of generative AI. As a matter of fact, their expertise often goes back decades before AI was defined as an umbrella term.
Startups Using Generative AI
Generative AI is being applied in many different industries. There are startups using generative AI in the fashion industry and the art world, for example, where brands and artists can create original designs that look like human artists created them. Such is the case of Lalaland.ai, a Dutch startup that provides a self-service platform where users can create their own hyper-realistic AI-driven fashion avatars in just minutes. Users may customise the virtual models' size, body type, shape, and identity—even down to whether they are happy or sad.
In the financial sector, banks are using generative AI to automate tasks such as checking account openings and loan approvals. And more than one startup has already begun applying generative AI to create virtual assistants who can respond appropriately to human requests with natural language processing and dialogue management capabilities.
The gaming industry is home to many startups and companies using generative AI algorithms. In fact, gaming companies have always strived to create realistic representations since the beginning. Most video game companies are involved in generative AI in some form. NVIDIA has developed generative adversarial networks that can do some incredible things. For example, GANs can reproduce a version of Pac-Man without prior knowledge of the game. Another type can animate facial expressions automatically, learning as it does so from real examples rather than being programmed to do this.
Others shine, however, because they rely heavily on AI. Using voice cloning technology, Respeecher provides advertising and entertainment businesses with interactive audio. Their machine-learning technology learns all of a voice's parameters before rendering a new dialogue using that voice.
With Rephrase.ai, Synthesia, advertisers and salespeople can create customised and personalised sales pitches using full text-to-video solutions. Using their tools, they begin with models that learn the moves of a person's face based on each phoneme and use them to create synthetic videos. They also maintain a collection of stock models. Some are generated by celebrities who license their image.
In D-ID, all lessons learned from creating deep fakes are applied reversely. An actual video of a person is taken, and the most recognisable characteristics are removed, such as the position of the eyes or the shape of the nose, for privacy purposes. The video is anonymised while retaining its main message.
In Rosebud ai, algorithms build human models and worlds from text descriptions to match requests. People explore ideas using their tools and then see how they are rendered. Versions of the apps are available for iOS and Android devices. Some of their creations are also being packaged as non-fungible tokens (NFTs), which are resold on cryptocurrency exchanges.
Another successful startup using generative AI is Stable Diffusion, which is a text-to-image diffusion model capable of generating photo-realistic images given any text input, thereby cultivating autonomous freedom to produce incredible imagery.
The artistic possibilities multiply thanks to DALL-E-2. You will be able to obtain designs that respond to your ideas just by writing them, but you can also edit existing images. The ability to add new objects or elements and easily substitute one for another is part of the range of opportunities. All this, while the program considers the lights and shadows, textures and reflections of the original image, offers a complete editing experience.
Finally, GPT-3 is an important artificial intelligence model for generating written language. Thanks to this algorithm, the user only has to start writing a paragraph and the system itself takes care of completing the rest in the most coherent way possible. Its great potential is a sample of the possibilities that exist to reach a general artificial intelligence capable of learning intellectual tasks like people.
The Cons and Risks of Generative AI
As I mentioned in other articles, AI is used in many applications, such as virtual assistants, chatbots, and autonomous vehicles. While AI is generally considered a positive technology, some drawbacks are associated with it. Some people believe that AI will replace humans entirely, while others believe it will enhance human lives.
Here are the main challenges associated with generative AI:
- Security issues: Due to its ability to generate fake photos and images closely resembling the real thing, generative AI may increase identity theft, fraud, and counterfeiting cases. Deepfakes rely on artificial intelligence to generate realistic videos and photos that can be used to impersonate people or make them appear to be doing things they didn't do. In the past, deepfakes were known for putting celebrities into movies and TV shows. But now, the technology has become more accessible to everyday users, who use it to create fake celebrity porn and other types of content.
The problem is that this technology could be used for malicious purposes: to create fake news stories about politicians or celebrities, for example, or even to embarrass an enemy or bully someone online. - Concern over data privacy: Data privacy issues can arise from using generative AI in different industries, such as healthcare, since it involves collecting private information about individuals.
- Limitations in creativity: The neural net mindlessly uses past data as a template for future work, meaning that the output it produces is usually based on something that has already happened rather than anything genuinely creative. In short, AI systems lack creativity and originality. They cannot generate new ideas by themselves—they can only make associations based on the data fed into them by humans.
- Copyright issues: The main copyright issues in generative AI are the same as those in traditional creative works. In fact, Getty Images has banned the publication of AI-generated content over concerns that it could be held legally liable for copyright infringement. Also, a number of stock libraries have banned AI images after artists and photographers raised concerns related to the reasons mentioned above.
The most relevant concerns regarding copyright in generative AI are:
- Copyright infringement: regarding Getty Images concerns, copying another person's work without permission or attribution.
- Derivative works: creating a new work based on someone else's original idea. Anyone can create derivative works, whether they have permission from the original creator or not - but there are legal consequences if you use someone else's work without permission.
This threat (and ultimately truth) about generative AI stands as a sort of warning and caution for those taking advantage of generative artificial intelligence generatively to produce even more artificially intelligent output. It is a bit mind-bending, but that is what happens when we are still learning about the potential uses of this technology.
As I always say, the future of AI is hard to predict. We may end up with a planet where humans are scarce, intelligent machines have outsmarted and outnumbered them, or some combination of the two. But things could also turn out very differently. An advanced yet benevolent AI may lead us to solutions we have never imagined. Maybe robots will be nothing but helpers and aides to help us thrive in ways we could not before. Or maybe things will fall somewhere on the spectrum in between. It is too early to say for sure how successful generative AI will be and how much it will change our lives, but we have got cause for hope – as well as plenty of reason to remain wary.
What Are the Benefits of Generative AI for Businesses and Organisations?
There are many ways in which businesses can benefit from generative AI. The first and perhaps most obvious benefit is the ability to automate tasks that currently require human input. This can save the company money on labour costs and make its processes more efficient by removing any bottlenecks or delays that may occur when working with humans.
Another benefit is leveraging data from different sources and combining them into something new and unique. Generative AI can also be used for predictive analytics, which can help companies better understand their customers' needs and preferences so they can create products that cater to those needs.
Generative AI can also be used for content creation, such as creating articles or blog posts from scratch or modifying existing content to make it more engaging or relevant for specific audiences.
Businesses can now generate images, restore films, and build 3D or SaaS models and environments much faster and more cost-effectively using generative AI models than with older, outdated technologies.
There is a massive reason why big companies and businesses heavily invest and get benefits from generative AI.
With technology advancing, so does its ease of use. The most obvious use of generative AI is in the marketing industry, which is quickly becoming a popular tool for email writing, graphic design, and video creation. Natural language processing has now advanced to the point that generative AI can now understand human input and respond to it more accurately than ever before.
Generative AI is already being used to create more engaging and relevant ads, which can increase click-through rates and conversions. This kind of technology also allows companies to better understand their customers by identifying what messages resonate with them and why.
Therefore, this technology can more easily create high-quality email marketing campaigns, videos, and images. Moreover, as it learns and improves, its output quality will only improve over time. This makes it no wonder that it is becoming increasingly popular.
Other relevant applications include:
Improving customer experience
This technology can help you provide a better customer experience by creating more personalised products and services. For example, Netflix has used generative AI technology to create its own thumbnails or improve the recommendation algorithm for users to offer a personalised experience, which has been hugely successful for the company.
Increasing efficiency
Generative AI can help make your business more efficient by ensuring your employees have access to all the information they need at their fingertips whenever they need it. This means less time spent searching for information manually and more time spent doing what they do best – working on projects that are important for your organisation's success.
Creating new products and services
Generative AI allows you to create new products or services, mainly digital content such as images, videos, artwork, etc., without any programming knowledge. You simply provide some initial information about what you want the software to do and then let it do all the hard work for you getting impressive results with minimal effort.
What Can We Expect From Generative AI in the Coming Years?
It has been ten years of AI's golden era. It is still the early days for meaningful AI.
The field of generative AI is still developing but is promising as a creative approach. It has been one of the past decade's most successful machine-learning frameworks.
To understand how important it will be in the future, let's see where it stands today:
Generative AI may seem trivial today, but it could dramatically improve AI efficiency and reduce bias in the future. With the help of artificial intelligence, Google has developed a tool that can turn text prompts into high-definition videos. Another Big Tech company, Meta, recently announced its own text-to-video system.
Google AI updated an existing function, Imagen, to support video with its Make-A-Video generator. Meta's Make-A-Video generator replaces Make-A-Scene, which was a text-to-image tool.
Investors Nathan Benaich and Ian Hogarth, who authored the State of AI report 2022, said research on the subject had only just begun.
"Meta and Google announced a more rapid, quality jump in the DALL-E moment of text-to-video generation in September," the pair wrote in the report. Despite the early stages of the process of generating video, AI-produced images are becoming mainstream with tools like Stable Diffusion and OpenAI's DALL-E.
Apart from images, the technique can also be used to generate text through chatbots, automated articles, and speech.
Generative artificial intelligence is gaining significant traction among all large tech companies and many startups. AI, in this form, creates something new rather than simply analysing what already exists.
It is expected that in the future, these kinds of generative models could be adapted to, for example, allow architects to describe a building and have an AI model provide a walkthrough of the building in seconds.
Generative AI Could Improve Over the Years
In future versions, the script could also be written from a prompt with the OpenAI GPT-3 natural language model. It is possible to feed in a script and have the AI create the visuals based on the description in the text, and the AI could also create a full-length commercial for television.
But are there other uses besides creative arts and marketing?
According to Kramer, yes. "Generative AI is fascinating, and we already see early success in a variety of contexts. It is a promising trend that I expect will continue to grow."
The potential of generative AI goes beyond pretty pictures and videos since it can also analyse conceptual or abstract ideas. The use of generative AI, which helps remove bias from machine learning models, can deliver higher quality outputs and make the jobs of data analysts easier as part of the heavy lifting is done by generative AI.
The processing required for generative AI to achieve the desired result makes it one of the most intensive forms of artificial intelligence. As Google explains in its research paper on Imagen Video, it uses a process called "progressive distillation," which distils information more effectively. It will take a great deal of computing power to perform these advanced functions.
Given the recent incredible progress we have seen in generative modelling, we see massive potential for further improvement, Google's engineers say.
In addition, generative AI can significantly transform the creative industries by bringing about fundamental changes in the most basic use cases. An artist can already generate images or features for use in images using a Photoshop plugin.
Future games could use these techniques to create massive worlds that are customised to each player - even the dialogue of non-playable characters could be different. The tool could create product descriptions, synopses, or complete articles. Staying on the creative track, generative AI can be used to create music and improve it.
Automation is often the key driver for digital transformation projects, and these generative tools will aid companies on their journey. Globally, the AI market will reach $190 billion by 2025, with some estimates suggesting the market will hit $15.7 trillion by 2030. As organisations understand the value AI can deliver, we will see even more uptake of generative AI, which I am sure is playing and will continue to play a role there.
Final Thoughts
AI is the next frontier for many technologists, so it is worth keeping an eye on this development. There are endless possibilities with the way that AI can be used, and we could see new industries growing from this form of intelligence in the coming years.
As technology and AI continue to advance, researchers, designers, and engineers worldwide are pushing the limits of their respective fields of study, and these opportunities will only become more and more prevalent. As the general public, we must continue to be open-minded to innovative change while staying informed of discoveries so that our values and opinions may guide the future of AI in a positive direction.
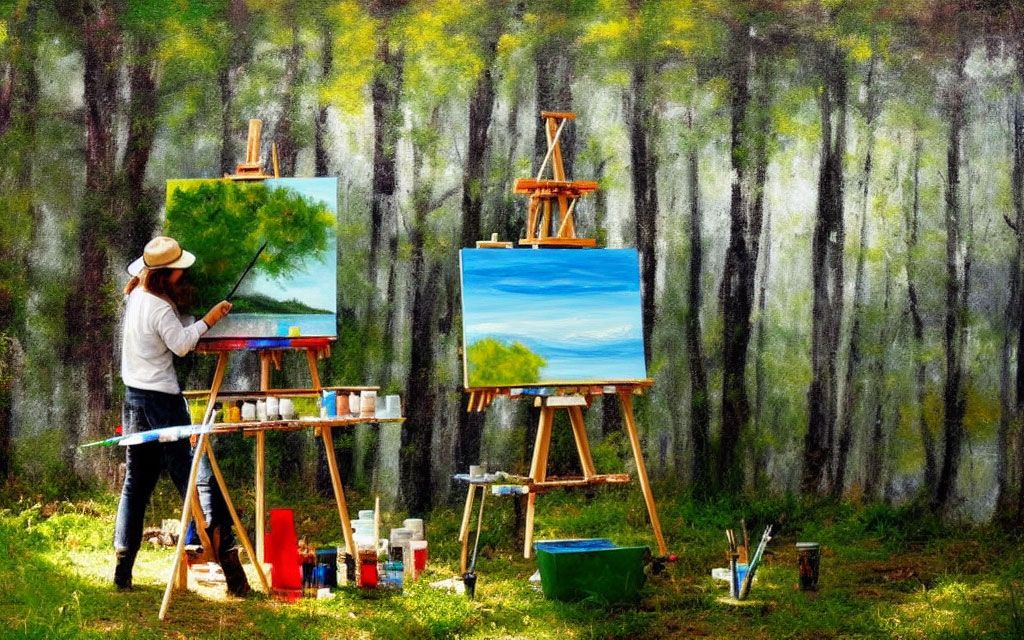
Cover image: Image created using Stable Diffusion with the text: "An artist at work painting a picture of nature"